What Are Jumping Spiders?
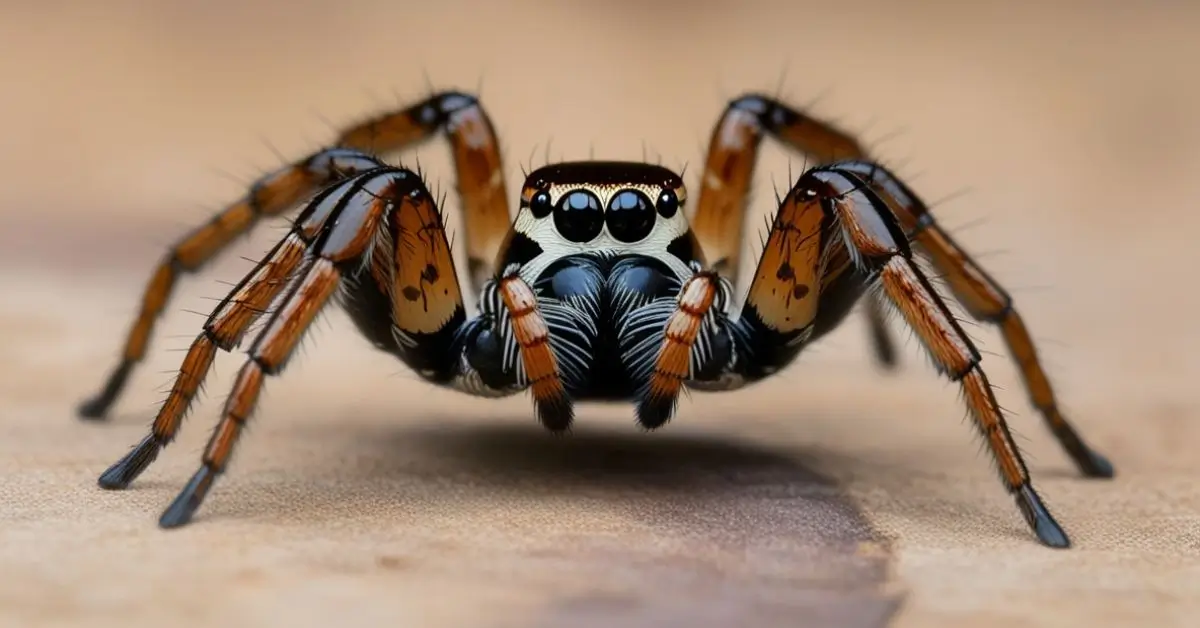
Jumping spiders are a unique group of spiders characterized by their jumping spider eyes and remarkable ability to leap distances many times their body length. These arachnids belong to the Salticidae family, which is known for the jumping spider’s distinctive body structure and excellent vision. Unlike other spiders that rely on webs to catch prey, jumping spiders are active hunters, chasing and leaping onto their arachnid prey. They are highly agile and rely on spider vision for detecting prey and navigating their surroundings.
These spiders are typically small, with many species measuring just a few millimeters in size. They can be found in a variety of habitats, from gardens and forests to even indoor spaces like homes and buildings. Despite their small size, jumping spiders are some of the most effective predators in the arachnid world.
How to Identify a Jumping Spider
To identify a jumping spider, look for its distinct features. The most obvious trait is its large central eyes, which are a key part of the jumping spider anatomy. These eyes give the spider excellent vision, allowing it to spot potential prey from a distance. Jumping spiders have a compact, robust body with long, spiny legs, which help them move swiftly and jump. Their bodies are usually covered in fine hairs, which can give them a fuzzy appearance.
The coloration of jumping spiders can vary greatly depending on the species, with some being brightly colored or having unique patterns. This coloration can serve multiple purposes, from camouflage in their natural habitats to attracting mates during their courtship dance. If you’re lucky, you might witness a male spider mating dance, where the male will display colorful markings to impress a female.
Key Characteristics of Jumping Spiders
One of the most defining characteristics of jumping spiders is their superior vision. They have four pairs of eyes, with the largest pair at the front, giving them near 360-degree vision. This extraordinary vision helps them detect both predators and prey, even in low light conditions. Their vision is so sharp that they can identify and track insects with ease, making them highly efficient hunters.
In addition to their exceptional eyesight, jumping spiders are also known for their ability to jump. They use a unique combination of muscular and hydraulic systems to propel themselves in impressive leaps. This helps them capture prey, avoid predators, and navigate their environment with precision. The combination of these traits makes jumping spiders one of the most interesting species in the spider world.
What Do Jumping Spiders Look Like?
Jumping spiders are small but mighty, with a characteristic body structure that sets them apart from other spiders. They have a broad, slightly flattened body, and their large central eyes give them an intense, almost curious look. Their coloration varies from drab browns and grays to vibrant oranges, blues, and greens, especially in males during the breeding season. This coloration is not just for decoration but plays an important role in their courtship behavior and in some cases, camouflage.
Jumping spiders have relatively short legs compared to other spiders, but these legs are powerful and allow them to leap distances greater than their body size. The jumping spider size varies, with some species measuring only a few millimeters, while others can grow up to 2 cm in length.
Where Do Jumping Spiders Live?
Jumping spiders can live in a wide range of habitats. They are commonly found in gardens, forests, and even indoor environments like houses and buildings. Jumping spider habitats are typically places that provide abundant prey and shelter, such as trees, shrubs, and even urban areas. These spiders are particularly fond of small cracks and crevices, where they can hide when not hunting.
One fascinating fact about jumping spiders is that they create spider retreats, which are small shelters they build in hidden spots. These retreats help them stay safe from predators, particularly at night when they are more vulnerable. The jumping spider’s adaptability to various environments makes it one of the most widespread and successful spider species.
Jumping Spider Behavior: What You Need to Know
Jumping spiders are highly active, spending most of their time hunting or exploring their surroundings. Unlike many other spiders, they do not rely on webs to catch prey. Instead, they use their incredible jumping spider movement to ambush and hunt arachnid prey. Their nocturnal behavior makes them more active during the evening and night, although some species also hunt during the day.
One of the most interesting behaviors of jumping spiders is their courtship dance. During mating season, males will perform a delicate dance to attract females. This involves waving their legs and displaying bright colors, a behavior that highlights the role of jumping spider silk in mating rituals. Their communication methods are intricate, relying on visual signals and vibrations to convey messages.
How Do Jumping Spiders Grow?
The life cycle of a jumping spider consists of several stages. They begin as spider eggs and hatch into tiny hatchlings. These tiny spiders go through a molting process several times as they grow. Each time they molt, they shed their exoskeleton and grow larger. Jumping spiders grow rapidly, and within a few months, they can reach their adult size.
As they mature, jumping spiders become more skilled hunters, relying on their vision and agility to hunt insect prey. They also undergo a final molt before becoming fully adult, ready to mate and continue the life cycle.
The Lifespan of Jumping Spiders
The jumping spider lifespan varies depending on the species, but on average, these spiders live for about one to two years. Their lifespan can be affected by factors like food availability, environmental conditions, and the presence of predators. Jumping spiders generally have a shorter life expectancy than larger spider species, but their agility and predator avoidance tactics help them survive long enough to reproduce and complete their life cycle.
What Do Jumping Spiders Eat?
Jumping spiders are insectivores, meaning they primarily feed on insects. Their diet includes flies, ants, moths, and other small arthropods. They rely on their sharp jumping spider eyes to detect prey and then stalk it before launching a leap to capture it. Their hunting technique is fast and precise, and they often hunt during the day when prey is more active.
Because of their role in controlling insect populations, jumping spiders play an important part in insect control. By keeping insect numbers in check, they help maintain the balance of ecosystems in both urban and natural settings.
Jumping Spider Infestation: Signs You Should Watch For
While jumping spiders are not dangerous to humans, their presence in large numbers can sometimes be a sign of a spider infestation. These spiders are often found in homes with ample insects to hunt. Signs of an infestation include seeing spider silk or noticing the spiders themselves in corners, windowsills, and other sheltered areas. If you’re concerned about a jumping spider infestation, the best approach is to seal cracks and crevices, reducing their access to your home.
How to Keep Jumping Spiders Out of Your Home
To prevent jumping spiders from entering your home, start by sealing all entry points. Use weatherstripping on doors and windows and check for cracks in walls or floors. Cleaning your home regularly can also help deter these spiders, as they are attracted to places with abundant prey. Keeping your environment tidy and well-maintained is key to keeping these spiders at bay.
Why Are Jumping Spiders Important to the Ecosystem?
Jumping spiders play a crucial role in the ecosystem as invertebrate predators. They help regulate insect populations, which can prevent the spread of pest species. Additionally, jumping spiders provide food for a variety of other predators, creating a balance within the food chain. By keeping insect populations in check, they contribute to the health of plants and other organisms in their environment.
Top Facts About Jumping Spiders You Didn’t Know
- Jumping spiders have incredible spider vision that allows them to see in high definition.
- The jumping spider bite is usually harmless to humans, with only mild irritation.
- Males perform a male spider mating dance to attract females during mating season.
- Jumping spiders are found in a variety of habitats across the USA, including urban and natural environments.
- They are known for their remarkable spider silk use, which helps in creating shelters and hunting.
Conclusion:
Jumping spiders typically live for 1 to 3 years, depending on their species, environment, and diet. These fascinating arachnids go through a unique molting process as they grow, and their eyesight plays a crucial role in their ability to hunt and detect prey. While their lifespan may be short, jumping spiders are effective invertebrate predators that help control insect populations. Understanding their life cycle and behaviors enhances our appreciation of their role in the ecosystem and their remarkable predator avoidance strategies.